Photoperiodism is the effect of duration of light on living organism. It is also defined as the effect of photoperiod (duration of light) on living organism for inducing certain physiological activities like flowering and growth. It was first discovered by H.A. Allard & W.W Garner in 1920 A.D. It shows adverse effect on plant as compared to animal. In plants it either induce or reduce flowering as per the availability of duration of sunlight. Due to photoperiodism and its effect, plant only induce flower in certain season of the year.
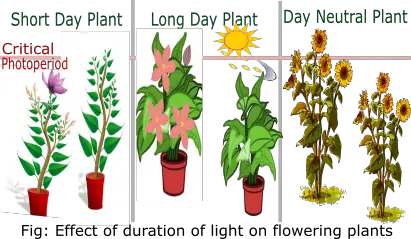
Photoperiodism in Plants
The pigment called phytochrome/chromoprotein is responsible for photoperiodism which detects the duration of sunlight in plant. It acts as signal for detecting the suitable season for inducing flowering in plants. Based on the length of photoperiod, Allard and Garner classified plants into 3-types.
- Short Day Plants
- Long Day Plants.
- Day Neutral Plants
Short Day Plants
The plants which require short duration of sunlight for flowering are called short day plants. It requires about 8-10 hrs. of sunlight. This type of plants are also called long night plant as they prefer short day and need not to exceed critical photoperiod. Short day plants flower in winter season due to short length of day and long duration of night which is favorable condition for flowering.
Examples of Short Day Plants
Examples of short day plants are: tobacco, sugarcane, strawberry, Brassica campestris (mustard), soyabean, Salvia, Cannabis, Chenopodium etc.
Long Day Plants
The plants which require long duration of sunlight for flowering are called as long day plants. It requires about 12-14 hrs. of sunlight. This type of plants flowers in summer season due to long duration of day and need to exceeds critical photoperiod which is favorable condition for flowering.
Examples of Long Day Plants
Examples of long day plants are: Beta vulgaris (beet), Triticum aestivum (common wheat), Raphanus sativus (radish), Spinacea oleracea (spinach) etc.
Day Neutral Plants
The plants which require equal duration of day and night for flowering are called as day neutral plants. This type of plant flowers in all season and lies within critical photoperiod.
Examples of Day Neutral Plants
Examples includes: Gossypium sps.(cotton), Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato), Helianthus annus (sunflower), Cucumis sativus (cucumber), Zeya mays (maize) etc.
Critical Photoperiod
Critical period is the period of sunlight which should or should not exce;ed for initiating flowering in plants. Long day plants require long duration of sunlight for flowering and thus the duration of sunlight must exceed the critical period. But in case of short day plants, it requires short period of sunlight for initiating flowering which does not exceed critical photoperiod. In short, long day plants must exceed critical photoperiod for flowering while short day plants should not exceed critical photoperiod for flowering.
Some plant needs both long and short duration of sunlight in their early development stage. Example: wheat.
Importance of Photoperiodism in Plants
Photoperiodism plays significant roles in plants. Important roles includes:
- It helps plants to induce flower on arrival of suitable season.
- From beginning, it is helping farmers for cultivating seasonal fruits and vegetables.
- From knowledge of effect of photoperiodism in plant, it has been easier for cultivation of off seasonal vegetables under green house and under controlled conditions.
- It helps plant breeders for crossing different photoperiodic plants for producing high yielding and all seasonal flowering and fruiting plant species.
Quick facts
- Phytochrome is the pigment responsible for photoperiodism in plants.
- Scotoperiod is the length of night or dark.
- The intensity and duration of sunlight is one of the factors causing bird and fish migration.